Soothing the Ache: Effective Strategies for Elbow Pain Relief
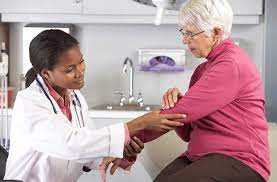 Elbow pain can occur from sports injuries, long periods of hard labor or due to aging. These injuries can damage tendons, bones and muscles within the elbow.
Elbow pain can occur from sports injuries, long periods of hard labor or due to aging. These injuries can damage tendons, bones and muscles within the elbow.
An expert elbow injury specialist Los Angeles will diagnose the condition and recommend an effective treatment. Your doctor will review your medical history and perform a physical exam.
Many types of elbow pain can be treated with corticosteroid injections. These injections are a fast, simple treatment that may provide quick and lasting pain relief. When you arrive at the doctor’s office, he or she will numb your elbow with a spray or anesthetic before inserting the needle. The doctor will use ultrasound or a type of X-ray called fluoroscopy to guide the needle into the correct location.
Prolotherapy works to strengthen the ligaments and tendons that support your elbow joint. The therapy stimulates a natural inflammation response that boosts healing, and it also increases the deposition of new collagen, which helps your ligaments and tendons become stronger.
If conservative treatments fail to relieve your elbow pain, NEIL GHODADRA, MD, can perform surgery to treat the underlying cause of your pain. To learn more about the treatment options available to you, call or book your appointment online today. We have convenient locations throughout Southern California.
The elbow is one of the most complex and often abused joints in the body. Because of this, it is susceptible to a number of orthopedic conditions that can cause pain and restrict motion. These conditions include tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis), arthritic changes of the joint, and bursitis, which is the inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs in the joint called bursae.
The doctor can also use arthroscopy to remove bone spurs, which are bony growths that pinch the ends of the bones in the elbow and restrict movement. This procedure is known as debridement and is commonly used for patients with posttraumatic or primary osteoarthritis of the elbow.
Regardless of the type of surgery, it is important to get plenty of rest after your operation and keep the elbow elevated as much as possible in order to reduce swelling. Your doctor may also recommend specific exercises to facilitate movement and strength in the elbow joint.
The elbow is a joint that’s used heavily for many activities, and it can become inflamed with repeated stress. Fortunately, most cases of elbow pain are caused by tendon problems or a simple injury, which can be treated with a few basic techniques and self-care.
The most common causes of elbow pain are tennis elbow and golfer’s elbow, which occur when the tendons that attach to the elbow bone on the outside (lateral) or inside (medial) of the arm become inflamed and damaged. These conditions are called “epicondylitis” and they often develop because of repetitive motions such as holding a racquet or golf club, or using force to hold a heavy object for long periods of time.
A doctor can diagnose these conditions with a physical exam of the elbow and wrist. They can also order imaging tests, such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to see the condition of the tendon and other structures in the elbow.
A healthy elbow bursa is a thin fluid-filled sac that reduces friction between bones and other parts of the elbow joint when you move your arm. If your elbow bursa becomes inflamed, it will swell and feel painful.
Most bursitis symptoms are caused by overuse or repetitive motion. This is why it’s important to change the way you use your elbows and avoid activities that put pressure on your bursa.
Symptoms of a bursal infection include pain when you bend your elbow or touch it, redness or warmth, tenderness and drainage of pus. Infected bursae often require antibiotic treatment to clear up the infection. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections may also help relieve elbow bursitis symptoms by releasing growth factors that promote healing in the area. To get PRP injections, blood is drawn from your arm and placed in a centrifuge that spins at high speeds. This separates the different layers of your blood, including a thin layer that is rich in platelets.

